What is a Sectioner?, and What Types Does it Have?
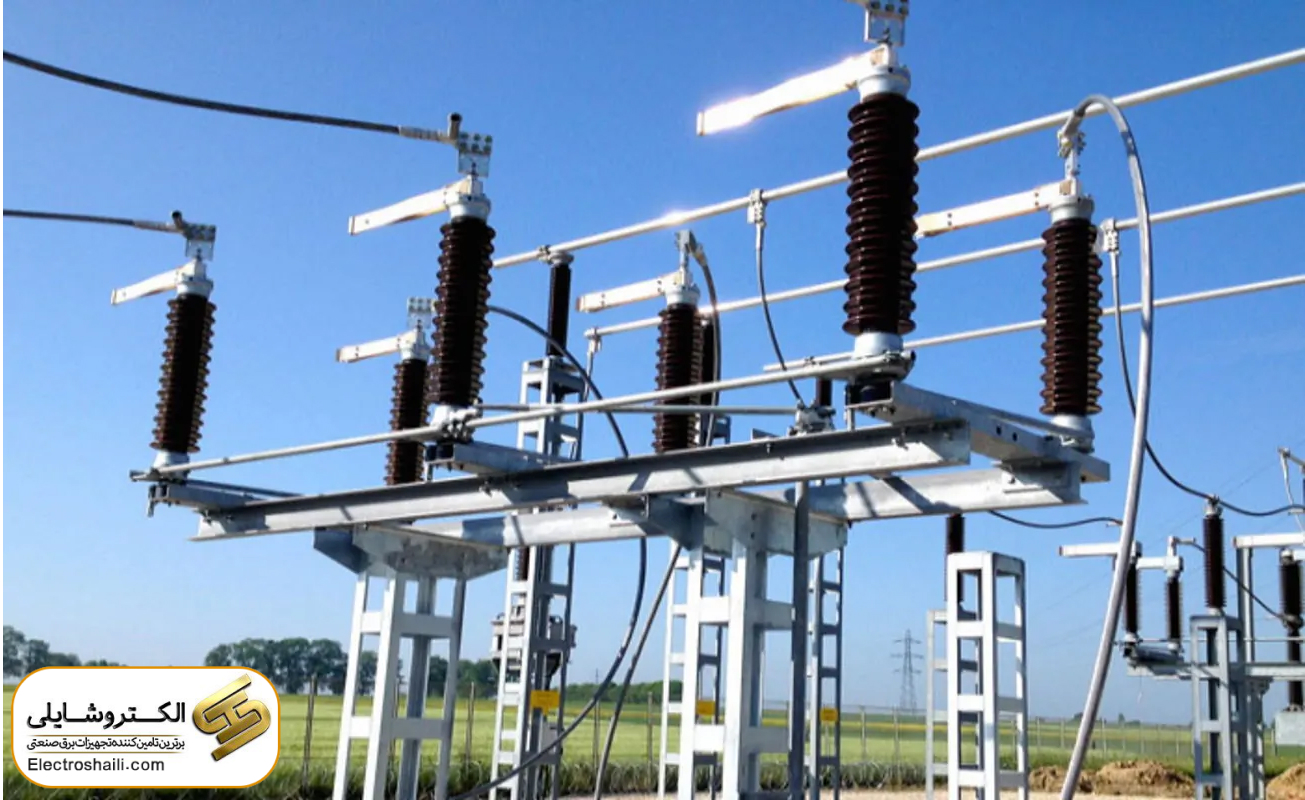
Electrical substations are equipped with various tools and devices to enhance the performance and safety of the power grid. One crucial equipment in these substations is called a “Sectioner.” This device operates with high pressure in electrical substations and is responsible for isolating and redirecting the flow of electrical current. There are different types of sectioners, each with its own characteristics and specific applications in this field.
With technological advancements, sectioners with more features are introduced to the market. Some of the applications of this device include automatic network management, system efficiency improvement, and prevention of unnecessary disconnections and reconnections. In this article, we will explore the various types of sectioners and their applications, providing comprehensive information in this area.
What is the Concept and Application of a Sectioner?
A Sectioner, also known as a Disconnector, is considered a type of power switch. The visible blades of these switches make them easy to identify. Different types of sectioners exist, classified based on their capability to disconnect under load or not.
This electrical device disconnects equipment and components that are under voltage. In other words, sectioners have the ability to disconnect and reconnect systems without current flow. But why are they used in high-pressure substations? The primary reason is that these devices separate various components of the substation from each other. It’s important to note that sectioners can disconnect low-voltage power cables, busbars, and transformers. Additionally, they contribute to improving insulation.
In essence, these power switches act as mechanical isolators or connectors between systems. Their main purpose is to prevent the risk of electric shock. Sectioners are mainly used during inspections, repairs, and generally in tasks related to high-pressure equipment.
Introduction to the Components of a Sectioner in Detail
In the complex world of electrical equipment, sectioners are recognized as vital devices. One crucial aspect in designing these devices is the characteristics of their contacts. To maintain optimal functionality, contacts in the closed position must have low resistance, and their temperature should not exceed 90 degrees Celsius during current flow.
This important device consists of three main parts: the supporting structure, current-carrying blades, and the operating mechanism with corresponding levers. Special attention is given to the care of contacts because oxidation is possible during disconnect and reconnect operations. Therefore, high mechanical resistance and contact material resistant to oxidation are essential for the contacts.
The operating mechanism of a sectioner can be manual or motorized. In the motorized mode, an electric motor is connected to the gearbox system, and levers cause the sectioner to open and close. This combination of components enhances the efficiency and performance of this vital device.
Wide Application and Importance of Sectioners
Sectioners serve as vital devices in the realm of electricity and have various applications. One of their fundamental roles is to ensure that the consumer is informed of the electrical device’s disconnection from the circuit.
In designing these devices, a critical point is that the cutting and breaking point should be clearly indicated during the disconnect and reconnect operations. This feature is crucial for the consumer to easily understand the status of the device and ensure their safety.
The main use of these devices is to isolate sensitive equipment and ensure safety against electrical current. This action prevents the use of equipment in dangerous conditions. The capacity weakness of sectioners is also created due to the reduced likelihood of being placed in the circuit after current disconnects by some equipment.
Introduction to Types of Sectioners
In the complex world of electrical equipment, sectioners are divided into two main categories based on their installation location: Indoor for installation inside buildings and Outdoor for installation in outdoor environments.
Furthermore, these power switches are divided into various types based on voltage levels and specific functions they have. Below, we will become familiar with different types of sectioners, each with its unique features and applications.
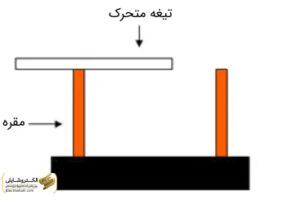
- Sliding Sectioner
Sliding sectioners, as one of the advanced types, are used for shallow racks or kiosks. These devices operate in a vertical direction, managing the disconnect and reconnect of electrical currents. Designed for medium pressure, they have a structure with two fixed legs and a movable blade. The length of the blade’s movement is a notable feature, and it can even be shaped like a tube, providing an additional practical advantage.
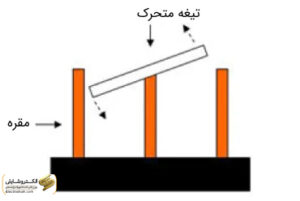
- Blade Sectioner
Blade sectioners serve as advanced technology for low to medium voltages. This type of sectioner is highly efficient in locations with limited surface exposure. Additionally, it can easily switch between two types: belt and profile, depending on the expected current flow.
Leveraged blade sectioners are also used to withstand strong pressure and extra-strong pressure. The installation type of this device should be such that it can easily connect and disconnect in adverse weather conditions. In the structure of these sectioners, a fixed contact and a movable contact are present, enhancing the performance and reliability of these electrical devices.
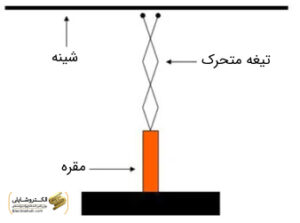
3. Sectioner Rotary
Rotary sectioners, capable of operating in the voltage range of 60 to 765 kilovolts, are used as an electrical advancement. This type of sectioner has two movable and rotatable blades that prevent untimely connection by resisting the forces of weight and wind.
During the operation of disconnecting or connecting, the bases of rotary sectioners rotate around their axis by 90 degrees. This rotation leads to the disconnection and connection of contacts, effectively preventing interference from external forces. By using rotary sectioners, the disconnecting and connecting operations are performed optimally in different environments.
4. Lever Sectioner
Lever sectioners, with the ability to cover voltage levels between 63 to 765 kilovolts, are essential tools in power flow management. These devices, with a tubular blade for each phase in the voltage range of 63 to 230 kilovolts and two tubular blades for voltage levels of 145 to 765 kilovolts, provide high flexibility in executing electrical operations.
The unique structure of these sectioners ensures reliable and safe performance in various voltage variations. The use of tubular technology in each phase makes these sectioners suitable for power transmission and distribution in different environments and various voltage levels.
5. Pantograph or Pantoagraphic Sectioner
Pantograph or pantoagraphic sectioners, as an advanced type of energy management technology, operate in high-pressure and extra-high-pressure voltages. These intelligent tools perform exceptionally well in locations with specific height differences and handle high pressure with precision and confidence.
By utilizing pantograph technology, these sectioners improve the network’s performance in various conditions. The wide-ranging applications of this type of sectioner in the energy industry and environments with different topographical features underscore their importance in optimizing power network performance.
6. Fused Load-Break Sectioner
Fused load-break sectioners, also known as load-break switches, provide the capability to disconnect current flows with multiples of the rated current. These sectioners, available in indoor and outdoor types, optimize current flow in small branches and motor feeders. The use of this technology in the power grid enables precise control of current flows, enhancing network efficiency.
7. Grounding Sectioner
Grounding sectioners are used to increase safety in maintenance and repair work on the power grid. These sectioners provide additional safety by discharging excess loads when personnel are in contact with transmission lines and substation equipment. The blade structure of these sectioners enables safe operation in high-pressure environments.
Deployment of Sectioners in the Circuit
According to standards, for each power switch in networks of 1 kilovolt and higher, two sectioners are installed on both sides of the disconnect or power switch. It is crucial that sectioners are closed before power switches and opened after the switches. When sectioners are opened or closed, the circuit of charge capacitor lines and small distribution transformers is considered. Additionally, the voltage across the two ends of the switch will not change during opening or closing.
Comparison of Sectioners with Disconnectors
Although disconnectors and sectioners are both considered power switches, they have significant differences. For example, sectioners do not have the capability to disconnect the circuit as they are recognized as non-load-break switches. In contrast, disconnectors act as load-break switches in high voltages and can disconnect circuits under load. Also, sectioners operate manually, while disconnectors operate automatically.
Conclusion
The entire world of technology is constantly seeking solutions to complex problems, and sectioners are one of these magical solutions. These power switches, with visible blades, play a crucial role in isolating and disconnecting voltage equipment. They have various types, including load-break and non-load-break switches.
The main application of these power switches is to isolate voltage equipment and components. Some of their features include indicating the location of the cut or break during the disconnection and connection of current. The structure of these switches consists of three main parts: the base, the contact or blade, and the lever mechanisms.
Sectioners are divided into various types, including draw-out, blade, shearing, grounding, lever, rotary, and fused load-break sectioners. Each of these types has its own applications and features.