Functionality of Industrial Drives or Inverters
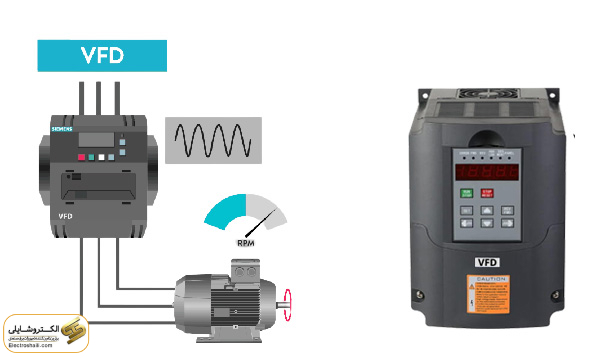
An industrial inverter, also known as a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), is considered a crucial device in the field of electrical industry. These devices act as controllers for voltage and frequency of the power supply, precisely regulating the speed of motors used in appliances and industrial machinery. They can also utilize internal battery tools for independent operation without the need for connection to the power grid when required. Additionally, due to the heat generated during operation, these devices often have cooling fans to maintain optimal temperatures.
The precise functionality of industrial inverters can significantly impact the overall system’s capabilities. By changing voltage and frequency, these devices enable motors to operate at various speeds and powers, providing businesses with greater flexibility in the performance of their machinery and equipment.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the applications and functionality of inverters, reading related articles and having a deep understanding of these devices is essential. This way, specialists and business owners can make the most of this advanced technology to enhance the performance of their systems.
Why Use Drives?
Power generation capabilities vary in drives. For safety, it is recommended to use a drive with a power rating about one-fourth greater than the required motor power.
Reducing current and energy consumption during startup is one of the reasons for using this equipment. Using a drive can generate maximum power for a short period and then reduce it to a lower level. Although the drive does not continuously operate at high power, it provides short bursts of maximum power.
Control of AC motor speed is one of the fundamental reasons for using industrial drives. An AC motor starts operating at full speed without a drive, and without an inverter, speed control of the motor is not possible. Inverters extend the performance range of motors compared to non-drive motors and constant-speed motors. Motor speed is measured in revolutions per minute, and speed change over a specific time is known as acceleration rate.
How Does a Drive Work?
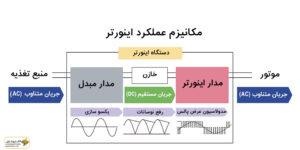
To better understand the internal structure of motor speed control, attention should be paid to some fundamental points. The output current of the power supply is provided in AC (alternating current). This current is converted to DC (direct current) by the internal converter or inverter. The inverter circuit, using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control, converts the converted DC current back to AC, generating a pulsed waveform.
These output pulses are applied to the motor coil to produce a sinusoidal current, accurately controlling the motor’s speed and torque. The images below show how the inverter operates:
In the first step, the converter circuit continuously converts the AC current into DC, a process known as rectification. The waveform’s direction and size change periodically over time, as the AC current creates a sinusoidal waveform. The diode acts as a semiconductor to create rectification by moving the electric current forward and converting it to direct current.
When the current passes through the diode, only positive current is transferred outward, creating a positive peak. However, the other half of the cycle passes in parallel, as negative current does not pass through. This process is known as full-wave rectification, as both peak waves change towards positive and negative.
However, full-wave rectification alone cannot create a smooth waveform, as the effects of AC current and voltage fluctuations remain. Therefore, capacitors alternately charge and discharge to reduce these fluctuations. The capacitor slowly brings the waveform closer to a smooth direct current and corrects it.
Modulation of Pulse Width in Drive Performance:
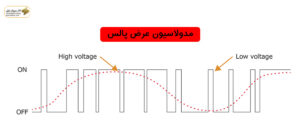
In the operation of a drive, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) stands out as a prominent technical term. In this process, the inverter circuit delivers AC current to the output through variable voltage and frequency. The output voltage of the inverter takes the form of a pulse wave, and these pulses are transformed into a sinusoidal current waveform by the motor winding, resulting in a sinusoidal current.
For this reason, the output of the inverter is not easily applicable to equipment other than motors. The mechanism of converting direct current into alternating current in this process creates pulse waves with different widths, controlled by power transistors such as “IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)” and ON/OFF variations through intervals.
The use of an inverter allows the adjustment and variation of AC frequency and voltage. This feature enables the control of motor speed and torque. This type of control, where voltage and frequency are freely adjusted, is known as Pulse Width Modulation or PWM.
Four Quadrant Drive Operation:
In the world of drive performance, we have the four-quadrant model. This model can be categorized as follows:
1. First Quadrant: In this stage, we have forward driving with positive speed and positive torque.
2. Second Quadrant: Here, we have braking and forward driving with positive speed and negative torque.
3. Third Quadrant: The third stage is also driving, but with reverse gear and positive speed, the torque tends towards negative.
4. Fourth Quadrant: In this stage, there is braking with negative speed and positive torque.
Applications depend on the type of load. Single quadrant loads usually operate in the first quadrant, including variable torque loads such as centrifugal pumps or fans and constant torque loads like extruders. Some loads operate in two quadrants, with positive speed and variable torque. Additionally, some loads operate in all four quadrants (first to fourth), where speed and torque are controlled in both directions; this includes elevators, escalators, and conveyor belts.
Soft Start and Stop of Motors Using Drive or Inverter:
Starting a motor using a drive or inverter is an intelligent method for optimizing the optimal performance of motors. In this process, the drive applies low voltage and frequency values to the motor, which allows precise control of the starting current surge. After the initial start, the frequency and voltage increase at a controlled rate, allowing the motor to provide optimal performance with up to 150% of its rated torque.
The stop sequence is also initiated in the reverse order of the start sequence. In this case, the frequency and voltage decrease to the motor with controlled reduction, gradually turning it off. Additionally, for reducing the load speed, a small amount of torque is available, and by adding a braking circuit, additional braking torque is obtained.
This braking circuit eliminates braking energy from the circuit, preventing excessive heat generation in the motor. Finally, the drive is equipped with a four-quadrant regenerative braking circuit, which allows braking the load by applying reverse torque and injecting energy into the AC line.
Advantages of Using Industrial Drive or Inverter:
Some of the main advantages of using inverters, which are used in various industrial fields, include:
– Increased motor lifespan: Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs or inverters) were introduced as a solution for optimizing energy consumption in industrial automation processes in the 1970s. These inverters, using PWM technology, can optimize the incoming electric current to the device and, consequently, significantly increase the motor’s lifespan.
– Energy savings: Reducing energy consumption and optimal use of power for a process are essential benefits of inverters. This feature ensures that the motor does not need to use its full power during an industrial process, significantly reducing energy consumption costs. Also, optimal energy consumption plays a crucial role in reducing motor wear.
– Fully adjustable speed: Another advantage of inverters is the ability to fully adjust the speed. These drives allow you to easily increase the speed of electric motors beyond their rated speed. Additionally, by connecting the inverter to temperature sensors, you can precisely control the speed and prevent motor overheating.
– Soft motor start-up: Using a variable frequency drive reduces the starting current and prevents the network from experiencing sudden pressure during motor start-up. This feature is known as soft start, and it is also achievable using a soft starter. However, there are differences between these two soft start methods, which are discussed in the article on the difference between inverter and soft starter.
– Speed control for industrial equipment: Another advantage of inverters is their efficiency in high-speed devices such as mixers, mills, and crushers, where the speed of these motors can be easily controlled. The use of variable frequency drives provides the possibility of creating no speed limitations, allowing for easy torque control.
– Other advantages:
– Reduced energy demand during peak times.
– Power reduction when not needed.
– Advanced overload protection capability.
– Controlled start, stop, and acceleration.
– Capability for dynamic torque control.
– Very simple installation process.
– High power factor.
– The possibility of creating smooth and impact-free movements for elevators and escalators using elevator inverters.
– Reduction of thermal and mechanical stresses on motors and belts during start-up.
With these advantages, the use of inverters in the industry is considered an advanced and efficient technology.
Conclusion:
The use of drives or inverters in the industry as a novel and efficient solution plays a crucial role in optimizing electrical processes. These technologies provide capabilities such as increased motor lifespan, energy savings, precise control of motor speed, soft start-up, and dynamic torque control.
Inverters allow effective energy use, reduce energy consumption costs, and improve the performance of motors. These advancements briefly indicate the beginning of a new era of efficiency and advanced control in the electrical industry.