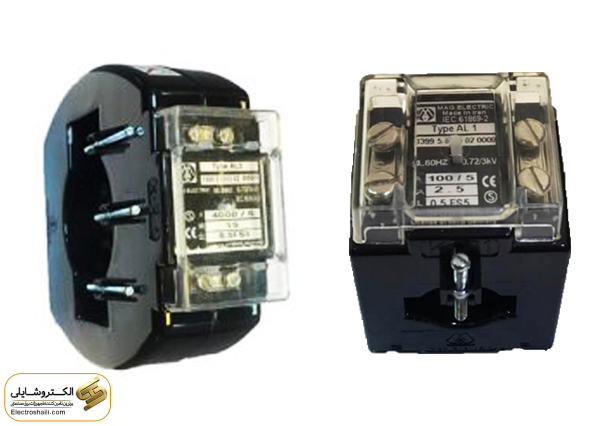
Current Transformer (CT): What is it and How Does it Work?
A Current Transformer, or CT, is a vital electrical device used in power transmission systems. This device samples high currents in high-voltage networks to provide accurate information about the current in different sections of the network. The operation of these transformers is based on the electromagnetic principle, and by changing the input current in proportion to the output current, they perform accurate sampling. Different designs of current transformers are used based on the specific needs of different networks.
Due to their high accuracy and reliable performance, current transformers are available in various sizes and appearances in the market. These devices play a crucial role in measuring both large and small currents and are used as an essential tool in various electrical power systems. The ability to select and use the appropriate type of current transformer in each electrical system is of great importance, and specialized consultation can greatly assist users in this regard.
What is a Current Transformer?
A Current Transformer, or CT, primarily works to convert high currents to lower values and isolate power networks. In power transmission networks, currents have high levels, making this transformer an essential tool for managing strong currents. For better understanding, it should be noted that CTs are installed in series circuits in high-pressure circuits.
This device is also known as a fundamental component of an ammeter and is used in measuring current in industrial electrical panels. In fact, current transformers play a vital role in the protection and measurement of isolated components in the power industry. These devices ensure optimal performance and safety of power systems.
Importance and Application of CT
CT, or Current Transformer, plays a very crucial role in network protection and current measurement. These transformers connect their outputs to measuring devices such as megohmmeters and ammeters, making the effectiveness and accuracy of measurement information crucial.
Current transformers with measuring cores must accurately match the nominal and normal current limits of the network to interpret measurement information correctly.
In line with network protection, the output of the current transformer is connected to protective relays. These relays require a current quantity and are responsible for creating ground connections, controlling current, and creating distance. This effective connection helps enhance the safety and efficiency of power networks.
Explanation of the Structure and Components of Current Transformers
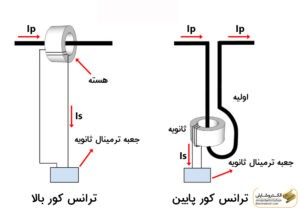
Every electrical device has a unique structure, and a current transformer is equipped with a specific structure. The Current Transformer, or CT, has two types of structures: core-balance and core-type, where the word “core” refers to the core. In the core-balance or high-core structure, the current core is located at the top, and its components include:
Secondary winding
Core
Outer casing
Insulating material
Low-pressure terminals
High-pressure terminals
How is a Current Transformer Installed?
These transformers are installed either externally or internally, with external installations occurring in AIS (Air-Insulated Substations) and internal installations in GIS (Gas-Insulated Substations). During installation, the secondary CT circuit must be connected to the ground. This connection should only be made at one point, as otherwise, without load on the secondary transformer, the risk of explosion exists.
It is essential to observe necessary precautions during the installation and connection of these transformers. Ensure that the direction of electrical current is correctly observed, and the current is sent towards measurement and protective equipment. Incorrectly observing the direction of the CT may lead to incorrect power measurement in the meter.
Exploring Types of Current Transformers
After getting acquainted with the definition of current transformers, let’s now delve into the types of these devices and examine the details of each.
Dry and Oil Current Transformers:
Current transformers can be categorized into two types based on their construction: dry and oil-filled. This classification is based on the type of environment surrounding the transformer core.
Instrument Transformers:
Measurement transformers or instrument transformers, known for their advanced features in the electrical field, are primarily used for measuring voltage and current in electrical equipment. In electrical installations, especially when there is a need to measure voltages exceeding 750 kilovolts, instrument transformers are employed. These transformers play a crucial role in accurately measuring voltages and may also have protective functions. Their structure consists of two cores made from primary and secondary windings.
Protective Current Transformers:
Protective current transformers are used to protect power sources, equipment, and relays. If the current passing through the circuit is 10 times the rated current, this transformer reacts immediately and becomes active. Protective transformers come in various types, including transformation ratio, accuracy class, permissible voltage, magnetic curve, and division power. Each type of protective transformer performs difficult and vital tasks with utmost precision.
Intervention Current Transformers:
Intervention current transformers are recognized as advanced technology in current measurement, usually used to reduce the measured current to a controllable level. The main purpose of implementing these transformers is to protect the circuit and accurately measure it.
In the secondary of these transformers, an alternating current is generated directly proportional to the primary alternating current. This type of transformer is ideal for situations where very high current is required for measurement. With this intervention approach, the transformer completely prevents adaptation and synchronization with various current conditions, providing protection and improving control within the measurement range.
Medium and Low Voltage Current Transformers:
This category of transformers is produced in open spaces or with different winding configurations and is used to convert the input current to a standard level.
High-Core Current Transformers:
High-core current transformers are advanced transformers that offer exceptional performance by having the core at the top of the structure. In this type of transformer, the conductor passes through a complex loop around the secondary winding. The winding wire inside this transformer is immersed in an oil-insulated environment, providing better performance and higher stability.
Low-Core Current Transformers:
In low-core current transformers, the conductor is placed inside a bushing, and the bottom part of the transformer is fixed in an oil-containing tank. This conductor is covered with paper and placed in an oil environment. The circular windings around this conductor become complex, and when current passes through it, the transformer heats up. This type of transformer is usually subject to sudden vibrations during operation. Therefore, it is not recommended for use in earthquake-prone areas.
Core-Balanced CT Transformers:
Core-balanced CT transformers are intelligent tools used to detect leakage faults in power networks. In single-phase circuits, phase and neutral wires pass through the core of the core-balanced CT, while in three-phase circuits, all phase wires along with the neutral pass through this transformer. This unique feature makes these transformers highly efficient for accurate current sampling, with a transformer ratio of 1 to 1000.
One of the prominent advantages of these transformers is the direct transmission of alarms from the problematic part. This feature ensures quick and accurate detection and resolution of faults. With the help of core-balanced CT transformers, prevention of serious damage to the power network becomes the top priority.
Introduction to the Specifications and Features of Current Transformers
Current transformers have unique features that are crucial to carefully consider. These features include:
1. Rated Primary Current: The maximum current covered by the current transformer.
2. Rated Voltage: The maximum working voltage that the current transformer can tolerate.
3. Accuracy Class: The measurement accuracy of the current measured by the transformer, which may vary based on different applications.
4. Magnetic Curve: The curve that defines the relationship between primary current and secondary current in the presence of a magnetic field.
5. Power: The transformer’s ability to transmit current considering various characteristics.
6. Transformation Ratio: The ratio of primary voltage and current to secondary voltage and current.
7. Selection of Current Transformers
To choose the most suitable current transformer, consider the following points:
1. System Specifications: Information such as maximum system voltage, system frequency, rated current, and type of system short circuit.
2. Intended Use: Determine the type of transformer based on protective or measurement use.
3. Usage and Environment: Environmental conditions such as installation altitude, maximum temperature, etc.
4. Type of Transformer: Determine the type of transformer, including current transformer and voltage transformer.
5. Accuracy Class: Determine the required measurement accuracy based on the transformer’s application.
6. Environmental Conditions: Take into account environmental conditions such as installation altitude and maximum temperature.
With these considerations, selecting the appropriate current transformer for your specific needs will be easier.
Finding the Best Current Transformers from a Reputable Store
Shaily Electric proudly provides all current transformer products from reputable brands such as Schneider Electric. These brands are ideal choices for engineers due to their outstanding and well-known quality in the electrical industry.
For purchasing and selecting the best current transformer, visit the Shaily Electric website and browse through our product catalog. Here, you can benefit from the variety and different types of current transformers with peace of mind.
Conclusion
We have discussed the most specialized current transformers in this article. These devices are not only used for current measurement but also for protecting equipment and relays. The unique features and structures of current transformers require your precise understanding.
These transformers are categorized into various types, including instrument transformers, protective transformers, high-core transformers, low-core transformers, and more. For a complete understanding of these vital equipment, it is recommended to become familiar with the features and applications of each category.