Surge Arrester: What is it? | Application, Function, and Types of Surge Arresters
Before addressing the question “What is a surge arrester?” we need to answer the following questions:
Would you prefer to spend 500,000 tomans or incur a loss of 20 million tomans?
Do you prefer using preventive measures against diseases and unpleasant incidents, or do you seek solutions to compensate for the damages after these incidents occur?
These questions may seem strange to you at the moment, and even the person asking them might doubt the meaning of these questions. However, it seems that the answers have been presented quite clearly. You might wonder who would choose the second option, i.e., incurring losses between 500,000 tomans and 20 million tomans? But if you wait a bit and stay with us, we will prove that many people, without awareness of this matter, choose the second option of incurring losses!
How? Let’s examine how this happens:
We are all familiar with thunder and lightning or lightning strikes. That current of several kiloamperes created when clouds rub against each other and generate an electric potential difference. We may feel joy and happiness at the moment of seeing rain and hearing the sound of thunder and lightning. However, often our attention does not reach beyond the fact that this high voltage difference must eventually find a way to discharge! And what better than our electrical and electronic devices for this purpose?
In fact, many of us, without knowing it, choose the second option, i.e., incurring losses, for our household, factory, and workshop equipment.
Instead of thinking about protecting ourselves before the incident occurs and creating a strong barrier against lightning at a lower cost than the damages, we often choose to soften the blow after these incidents.
What can create this powerful barrier other than a “surge arrester” or “surge protector”?
What is a Surge Arrester or Surge Protector?
A surge arrester or surge protector is prominent as a vital device in the field of electrical protection. This electronic device primarily aims to prevent the entry of excess voltages and transient currents resulting from phenomena such as lightning, switching, installations, and electrical, electronic, telecommunication, and radio equipment. This device protects facilities in adverse weather conditions and equipment even in unfavorable weather conditions.
How Does a Surge Arrester Work?
A surge arrester can limit and prevent the entry of sudden voltage increases, such as during a lightning strike, by diverting the current towards the grounding system. For a better understanding of the surge arrester’s operation, a simple comparison can be helpful. Imagine you have a water pipe. A sudden increase in water volume beyond the pipe’s tolerance causes it to crack. The same thing happens in electrical and electronic devices during a lightning strike.
Now imagine there is a valve inside the pipe that only opens when there is a sudden increase in water volume. The presence of this valve and the discharge of excess water current inside it reduce the load on the water pipe and prevent it from cracking and breaking.
What is the Difference Between a Surge Arrester and Power Protectors?
Power protectors are typically used before using electrical devices and mainly have the ability to control and limit voltage increases up to 15%.
These protectors deal with regulating voltages caused by fluctuations in electricity from external sources such as power companies and transformers. However, they are not capable of managing high voltages caused by lightning or switching. Therefore, using these electrical protectors alone is not sufficient to protect electrical devices from such voltage changes.
How to choose a suitable surge arrester?
To choose the best surge arrester, it is first advisable to familiarize yourself with the classification and various types:
Class B Surge Arrester
These types of arresters are used as primary protection at the building entrance against lightning strikes, with a withstand current of KA100. They are connected in parallel to power lines outside the building and are used to protect electronic devices, electrical installations, and electronic equipment against overvoltage or direct current from lightning. These arresters have high discharge capacity and are synchronized with a 10/350 microsecond waveform.
Additional Explanation:
As a result of lightning and switching, two different waveforms are created:
– 20/8 microsecond waveform (resulting from switching)
– 10/350 microsecond waveform (resulting from direct lightning)
Class C Surge Arrester
This surge arrester, when installed in secondary distribution boards and sometimes in main distribution boards, provides protection against switching events. It can also be used in the main distribution board to have the capability to connect to the electrical system and ground. The goal of this surge arrester is to reduce overvoltage in electrical devices. Equipment should be activated before the residual current device (RCD) to ensure that the RCD does not see the surge current as residual current and disconnect the circuit.
Class B+C Surge Arrester
This type of surge arrester provides the highest level of protection in situations where sudden overvoltage occurs. It is widely used in panel boards, telecommunications, industrial and military centers, and extensive electrical systems. These surge arresters dampen currents and overvoltages caused by lightning and also eliminate switching surges. They are designed with high flexibility and synchronize well with other surge arresters. An important note is that during the discharge of additional current, dangerous ionized gases are not produced.
Class D Surge Arrester
Class D surge arresters provide the final stage of protection and are installed to cope with inductive coupling and switching waves in the circuit of final devices, before power outlets and close to equipment. These arresters have lower voltage compared to other surge arresters and are therefore used for sensitive equipment such as televisions, refrigerators, computers, data centers, and fire alarm sources.
Data Surge Arrester:
In today’s world, data systems and information technology are widely used in various industries. These electronic systems that process information are crucial. Protecting these systems against hazards and preventing significant financial losses is highly vital. Data surge arresters are used in telecommunication systems, data transmission, closed-circuit cameras, fire alarm systems, etc., to prevent damages caused by sudden voltage increases.
Telecommunication Lines Surge Arrester:
These types of arresters are used to protect CAF5 and CAT6 cable lines. Telecommunication surge arresters are installed in the junction box for telephone cable distribution.
Closed-Circuit Camera Surge Arrester: Outdoor Security
One of the worst environments for electronic equipment is the outdoors, especially during lightning when serious damage can occur. Most closed-circuit cameras are also placed in these environments. Closed-circuit camera surge arresters are divided into two types: coaxial cable and LAN cable. They prevent damage to cameras in case of lightning in the signal and electrical communication path.
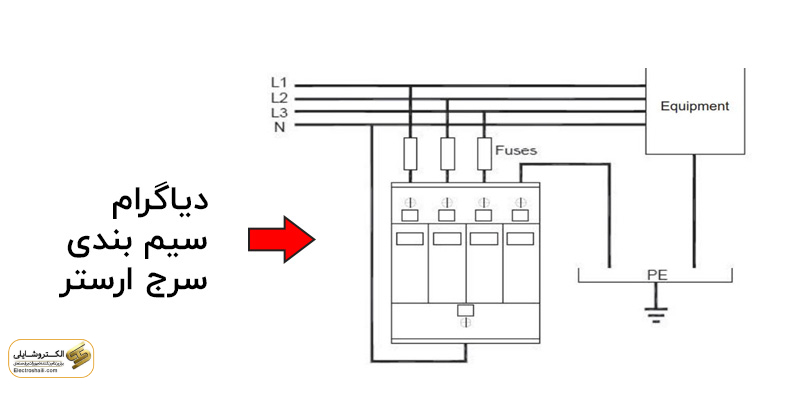
Installation of Surge Arresters in Circuits: Practical Guide
For the installation of surge arresters in circuits, you can use either series or parallel connection methods. The type of connection depends on the application requirements. In all cases, the surge arrester must be placed after the main switch and before the residual current device (RCD). Most models of surge arresters are modular, consisting of two parts: protective elements and base. Protective elements are inserted or attached to the base like a cap. In some cases, the base and protective elements are integrated and cannot be separated.
Surge arresters are produced in various types, including single-phase, phase and neutral, neutral, two-phase, two-phase and neutral, three-phase, and three-phase and neutral. Each of these types is used depending on the application and environmental conditions. The circuit and performance of surge arresters are independent of each other. In some cases, a fault in one of the phases does not disconnect the three-phase surge arrester installation line.
The lifespan of surge arresters depends on the number and intensity of lightning strikes or voltage surges caused by switching in the network.
In double-pole bases and higher, surge arresters merely connect the output paths to the ground to each other. This is done to reduce and optimize wiring routes.
Widespread Applications of Surge Arresters in Industrial, Commercial, and Residential Sectors
With coverage of the basic concepts of surge arresters, we now explore the applications and use cases of this equipment in systems.
Power Distribution Systems:
Surge arresters in power distribution systems are used as a protective ring against fluctuations and voltage increases.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC):
For the protection of programmable logic controllers used in various industries, surge arresters provide security and better performance.
Motor Controllers:
Control systems for motors use surge arresters to reduce the risks of sudden currents and additional voltages.
Lighting Circuits:
Surge arresters in lighting circuits serve as safety devices to prevent access to increased voltage.
Medical Equipment:
Surge arresters in medical equipment are used to protect against fluctuations and sudden currents.
HVAC Equipment:
To maintain ventilation and air conditioning equipment, surge arresters are used as a barrier against voltage increases in HVAC systems.
Process Control Systems:
In process control systems, surge arresters act as a robust response to voltage and current changes.
Industrial Power Outlets:
Surge arresters in industrial power outlets prevent the effects of lightning or voltage fluctuations.
Data Input Connections:
Protection of data input connections in communication systems, including telephone or fax lines, is one of the functions of surge arresters.
Communication Circuits:
Surge arresters in communication circuits and cable television lines are used to prevent the effects of sudden voltage increases.
Security Systems and Entertainment Centers:
In security systems and warning circuitry, surge arresters act as prominent protective rings.
Household Appliances:
Surge arresters are also used in household applications to protect electrical and electronic devices against voltage fluctuations.
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined the concepts and applications of surge arresters in industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. We first explained the concept of surge arresters and examined their role in protecting electrical systems against voltage and current fluctuations. We then explored the extensive applications of this equipment in various industries, including power distribution, motor control, medical equipment, security systems, and household appliances. Additionally, we discussed the installation cases and types of surge arresters along with relevant technical details.